Below is a simple example of Spring FileSystemResource.
First create an Address bean under src as shown below.
File: com.ram.beans.Address.java
package com.ram.beans;
public class Address {
private String street;
private String city;
private String state;
public String getStreet() {
return street;
}
public void setStreet(String street) {
this.street = street;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
}
Next create applicationContext.xml file under src. The file is given below.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="addr" class="com.ram.beans.Address"> <property name="street" value="Richmond"></property> <property name="city" value="Melbourne"></property> <property name="state" value="Victoria"></property> </bean> </beans>
Next create a main class under src as shown.
File: com.ram.app.FileSystemResourceExample.java
package com.ram.app;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import com.ram.beans.Address;
public class FileSystemResourceExample {
public static void main(String[] args){
Resource resource = new FileSystemResource("F:\\Blogger\\applicationContext.xml");
BeanFactory container = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
Object obj = container.getBean("addr");
Address address = (Address) obj;
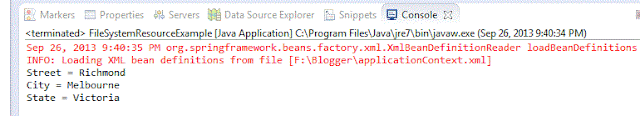
System.out.println("Street = "+address.getStreet());
System.out.println("City = "+address.getCity());
System.out.println("State = "+address.getState());
}
}


No comments:
Post a Comment